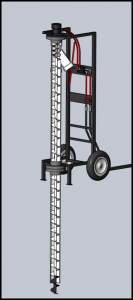
The Excrevator was developed to provide a user friendly and effective method for pit emptying in the developing world. The basic design models the common screw conveyor or screw pump used in the food processing and wastewater industries. The most recent version being developed during Phase II, as shown in figure on the left, consists of a hydraulic motor that rotates a screw within a stationary pipe. The hydraulic motor is powered by a gasoline engine, not shown in the schematic, that does not have to be next to the pit. The bottom of the pipe sits at the bottom of the pit and when rotated it would lift the waste up through the pipe and out through a tee fitting. Reverse flights just above the outlet directs the flow out of the tee and into transport containers. This design can rotate up to 500 rpm and has shown flow rates of up to 125 liters per minute. It also can be run in reverse to expel debris that may become lodged within the pipe. The dolly-like frame makes the Excrevator easy to maneuver up to and within the pit.
Since NC State is also a prominent agriculture university, we have plenty of access to animal poo! The video below shows us testing the Version 2 Excrevator (please excuse the poor quality) on a simulated pit full of dairy waste. The Excrevator preformed very well on this material with flows up to 125 lpm. The Dairy Farm setup has given us a great platform for full scale testing of the Excrevator before it is sent overseas for in-country testing.
At the end of our Phase I development, we were able to spend a week testing Version 2 of the Excrevator near Durban, South Africa in correspondence with Partners in Development. We gained valuable data and experience on the challenges with pit emptying. Although the Excrevator showed some promising success, we targeted some specific areas where the design could be improved. These include making the Excrevator more maneuverable, emptying dry pits (non-flowing), and dealing with trash that is also found in the pits. All of these issues are being addressed in Phase II through lab, field, and in-country testing.